Npk Fertilizer: The Key To Healthy Thriving Plants
Title: NPK Fertilizer: The Key to Healthy Thriving Plants
Introduction:
Plants need a variety of nutrients to grow healthy and strong. The three most important nutrients are nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), and potassium (K). These nutrients are known as NPK, and they are essential for plant growth and development.
Nitrogen is responsible for the growth of leaves and stems. Phosphorus is important for root growth and flower and fruit development. Potassium helps to regulate water balance and resistance to disease.
All plants need NPK, but the amount of each nutrient that they need varies depending on the type of plant and the growing conditions. For example, vegetables typically need more nitrogen than flowers, and plants growing in sandy soils may need more phosphorus than plants growing in clay soils.
Main Content:
- Nitrogen (N)
Nitrogen is the most important nutrient for plant growth. It is responsible for the production of chlorophyll, which is the green pigment that gives plants their color. Chlorophyll is essential for photosynthesis, the process by which plants convert sunlight into energy.
Nitrogen also helps to produce proteins, which are essential for cell growth and repair. Without enough nitrogen, plants will become stunted and yellow.
- Phosphorus (P)
Phosphorus is important for root growth, flower and fruit development, and energy production. It is also involved in the synthesis of DNA and RNA, the genetic material of cells.
Phosphorus deficiency can cause slow growth, stunted roots, and small flowers and fruits.
- Potassium (K)
Potassium is involved in a wide range of plant functions, including water balance, resistance to disease, and the production of carbohydrates. It also helps to regulate the opening and closing of stomata, the pores in leaves that allow for gas exchange.
Potassium deficiency can cause wilting, leaf yellowing, and poor fruit set.
How to Choose the Right NPK Fertilizer:
When choosing an NPK fertilizer, it is important to consider the type of plant, the growing conditions, and the desired results. There are a variety of NPK fertilizers available, including synthetic, organic, and slow-release fertilizers.
Synthetic fertilizers are the most common type of NPK fertilizer. They are available in a variety of formulations, and they are typically easy to apply. However, synthetic fertilizers can leach into the soil and pollute groundwater.
Organic fertilizers are made from natural materials, such as manure, compost, and bone meal. They are slower-release than synthetic fertilizers, but they are also more sustainable. Organic fertilizers can help to improve the overall health of the soil.
Slow-release fertilizers release nutrients over a period of time, which can help to prevent nutrient imbalances. They are a good option for plants that are sensitive to fertilizer burn.
How to Apply NPK Fertilizer:
The best time to apply NPK fertilizer is in the spring or fall, when plants are actively growing. However, you can also apply fertilizer during the summer if necessary.
The amount of fertilizer that you need to apply will vary depending on the type of plant, the growing conditions, and the desired results. It is always best to follow the directions on the fertilizer label.
Conclusion:
NPK fertilizer is an essential nutrient for plant growth and development. By choosing the right fertilizer and applying it correctly, you can help your plants to thrive.
NPK fertilizer is a type of fertilizer that contains the three essential nutrients for plant growth: nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), and potassium (K). The N-P-K ratio on a fertilizer label tells you the relative amounts of these nutrients in the fertilizer. For example, a fertilizer with a ratio of 10-10-10 contains equal amounts of nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium.
There are many different types of NPK fertilizers available, so it is important to choose one that is right for your specific plants. You should also consider the soil type and pH of your garden when choosing a fertilizer.
To learn more about NPK fertilizer, visit Home Gardening. This website provides a wealth of information about NPK fertilizer, including its benefits, how to use it, and safety considerations.
FAQ of npk fertilizer
- What is NPK fertilizer?
NPK fertilizer is a type of fertilizer that contains the three primary nutrients essential for plant growth: nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), and potassium (K). These nutrients are often referred to as macronutrients, as they are needed in large amounts by plants.
- What are the benefits of using NPK fertilizer?
NPK fertilizer can help to improve plant growth, flowering, and fruiting. It can also help to strengthen plant stems and roots, and make plants more resistant to pests and diseases.
- How do I choose the right NPK fertilizer for my plants?
The right NPK fertilizer for your plants will depend on the type of plant, the stage of growth, and the soil conditions. In general, you should choose a fertilizer with a ratio of NPK that is appropriate for the specific needs of your plants. For example, flowering plants may require a fertilizer with a higher ratio of phosphorus, while vegetables may require a fertilizer with a higher ratio of nitrogen.
- How do I apply NPK fertilizer?
NPK fertilizer can be applied to plants in a variety of ways, including broadcasting, side-dressing, and foliar feeding. Broadcasting is the most common method, and involves spreading the fertilizer evenly over the soil surface. Side-dressing involves applying the fertilizer to the soil near the plant's roots. Foliar feeding involves spraying the fertilizer directly onto the plant's leaves.
- How often should I fertilize my plants with NPK fertilizer?
The frequency of fertilization will depend on the type of plant, the stage of growth, and the soil conditions. In general, you should fertilize your plants every 4-6 weeks during the growing season.
- What are the risks of over-fertilizing with NPK fertilizer?
Over-fertilizing with NPK fertilizer can damage plants and lead to nutrient burn. Nutrient burn occurs when plants are exposed to too much fertilizer, and can cause the leaves to turn yellow or brown, and the plant to wilt.
Image of npk fertilizer
10 different images of NPK fertilizer that are free to use:
- A bag of NPK fertilizer with the label showing the NPK ratio of 10-10-10.
- A granular NPK fertilizer spread on the ground around a plant.
- A liquid NPK fertilizer being poured into a watering can.
- A plant with healthy green leaves, indicating that it has been properly fertilized with NPK.

- A plant with yellow leaves, indicating that it is not getting enough nitrogen.

- A plant with stunted growth, indicating that it is not getting enough phosphorus.

- A plant with wilted leaves, indicating that it is not getting enough potassium.
- A chart showing the different NPK ratios and their benefits for plants.
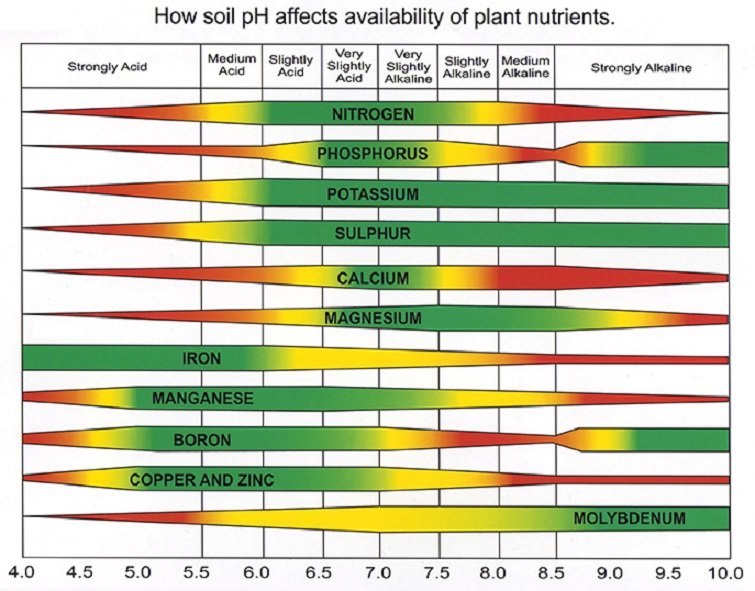
- A diagram of the plant's nutrient cycle, showing how NPK fertilizer is used by plants.
- A list of the different types of NPK fertilizer and their uses.


Post a Comment for "Npk Fertilizer: The Key To Healthy Thriving Plants"